Since more than one year ago, I have had really often discussion with current or new customers about type of vCenter deployment - vCenter Appliance (vCSA) or vCenter Windows Version. From vSphere 5.5, vCSA has been improved and practically does not differ from vCenter "Windows Version" now.
So why I recommend the vCenter Appliance? I'm not a Linux guy only, but also Windows as well 🙂 so this is not the reason 🙂
Deployment and perform an update/upgrade of vCenter
One of the coolest things of vCenter Appliance are:
- deployment - you can install and configure vCenter really fast
- update or upgrade to the newer version.
vCenter Appliance is shared as OVF template, based on pre-configured SUSE Enterprise Linux. You can deploy it in the same way as every virtual appliance provided by VMware.
Update or upgrade is really easy and useful - what you have to do is taking a snapshot of vCenter before performing an update or upgrade and go to the admin page of vCenter and Update or Upgrade tab:
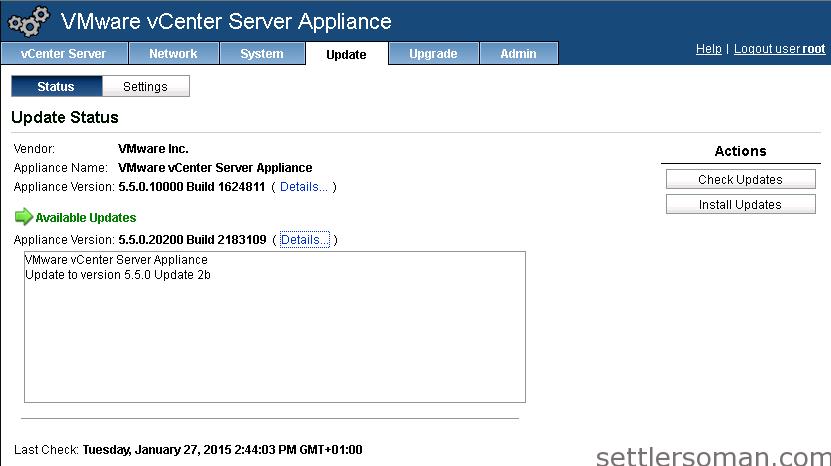 When the vCenter Appliance is connected to the internet, you only have to click Check Updates and then Install Updates. Easy, isn't it?
When the vCenter Appliance is connected to the internet, you only have to click Check Updates and then Install Updates. Easy, isn't it?
Unfortunately, VMware changed a way of updating VCSA in version 6...
Scalability
Before vSphere version 5.5 the vCenter Server appliance was limited (max 5 ESXi and 50 VMs). Currently, vCenter Appliance supports 100 ESXi hosts and 3000 VMs when you use embedded (vPostgreSQL) database. If you use external Oracle database, vCenter Appliance supports 1000 ESXi hosts and 10000 VMs.
vCenter Appliance does not support Microsoft SQL, when vCenter Windows does. But is this really a problem? In my opinion no, because an embedded database is enough for almost environment.
vCenter Server Additional Services
vCenter Server Appliance provides pre-installed following services:
- Auto Deploy
- Syslog Collector
- ESXi Dump Collector
- vSphere Web Client
- Single Sign-On
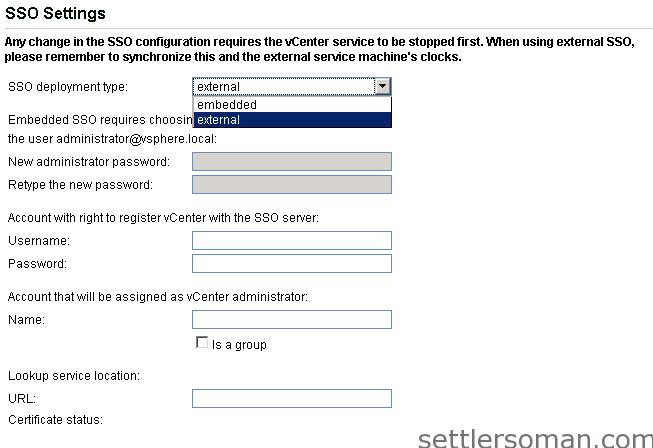
 All above services available in vCSA are not limited and provide the same functionality as on vCenter Windows Version. For example, if you need to use external SSO, vCenter Appliance supports it:
All above services available in vCSA are not limited and provide the same functionality as on vCenter Windows Version. For example, if you need to use external SSO, vCenter Appliance supports it:
Syslog Collector installed on Windows provides plugin for vSphere Client when on vCenter Appliance - does not. To check logs, you must log into the console or connect to vCSA using SSH. There is a similar limitation of ESXi Dump Collector on vCSA.
When to use vCenter Server installed on Windows Machine?
- when you have to use external database on Microsoft SQL Server,
- when you use VMware Update Manager (VUM) and you would like to have it on the same VM with vCenter (VMware recommends to install separate),
when you need to use Linked ModeUpdate: VCSA 6 supports it!when you need to use IPv6VCSA 6 supports it!
- when you want to deploy Site Recovery Manager (SRM) on the same VM with vCenter,
- when you have to install vCenter on physical server,
- when you want to install some additional softwares required by 3rd parties (backup, storage management etc or just vSphere PowerCLI).
As the conclusion of this post, please follow the below table where you can find a comparison vCenter Appliance and vCenter installed on Microsoft Windows:
| vCenter Appliance | vCenter installed on Windows | |
|---|---|---|
| OS | A pre-configured SUSE Enterprise Linux based virtual appliance | Windows 2008 r2 and later. Please follow VMware Product Interoperability Matrixes |
| Virtual or Physical | Only Virtual | Virtual and Physical as well |
| Embedded database | vPostgreSQL database (100 ESXi hosts, 3000 VMs) | Microsoft SQL Express database (5 ESXi hosts, 50 VMs) |
| External database | Oracle only (1000 ESXi hosts, 10000 VMs) | Oracle and Microsoft SQL Server as well (1000 ESXi hosts, 15000 VMs) |
| Auto Deploy | Pre-installed, not running by default | Optional, Need to be installed |
| Syslog Collector | Pre-installed, not running by default | Optional, Need to be installed |
| ESXi Dump Collector | Pre-installed, not running by default | Optional, Need to be installed |
| vSphere Web Client | Pre-installed | Need to be installed |
| Single Sign-On | Pre-installed | Need to be installed |
| IPv4 or IPv6 support | IPV4 and IPV6 as well | IPV4 and IPV6 as well |
| vCenter Update Manager | Need to be installed on external VM | Can be installed on the same VM or external as well |
| Site Recovery Manager | Need to be installed on external VM | Can be installed on the same VM or external as well |
| Linked Mode | Supported | Supported |
vCenter is a crucial component and should be protected as much as possible. What happens to your infrastructure when vCenter is down is described here.