This post covers a feature introduced in vSphere 5.5 - VMware vSphere Flash Read Cache (vFRC).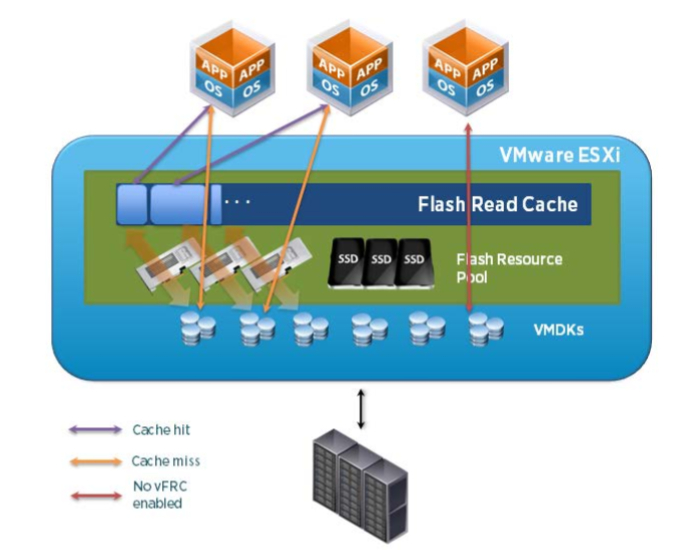
VMware vSphere Flash Read Cache (vFRC) is a feature that provides server side read cache from local solid-state devices (SSDs - PCIe flash cards or solid-state drives). By using local flash storage, vFRC creates a large, low latency read cache which can be used for critical application requiring high levels of physical reads.
There are following prerequisites of VMware vSphere Flash Read Cache (vFRC):
- vCenter and ESXi 5.5 or later
- Supported only vCenter Web Client (can only be configured with the vCenter web interface)
- Can only be configured on a virtual machine with hardware version 10 (VMX-10)
- The flash storage must be either SSD or PCIe flash card and must be unused (of course it must be listed on HCL)
The vFRC in vSphere 5.5 supports the following maximums for each ESXi host:
- One Virtual Flash Filesystem (VFFS) per host
- Eight flash devices per VFFS
- 4 TB maximum individual flash device size
- Maximum 400 GB of vFRC per VMDK
- 32 TB of total vFRC per host
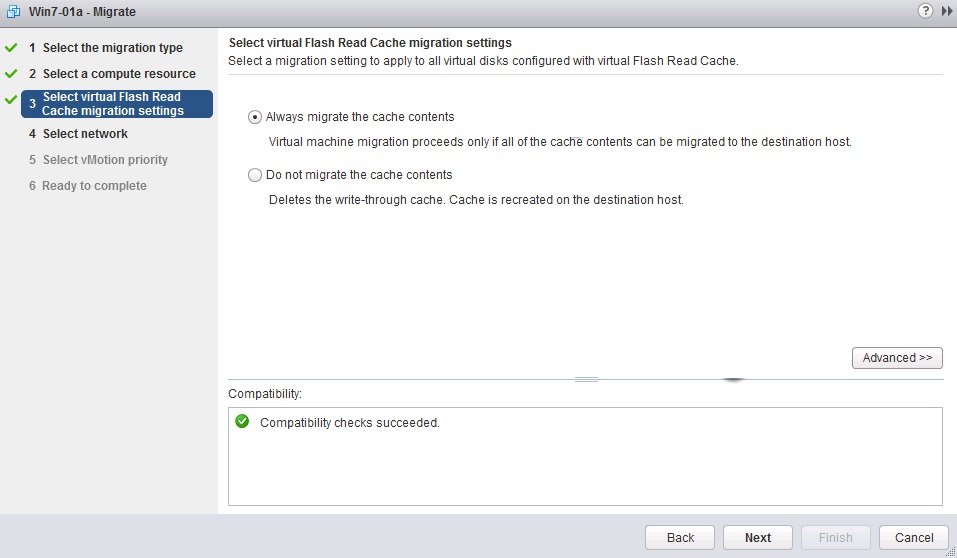
VMware vSphere Flash Read Cache is supported by vMotion and a VM can be migrated using the following options:
- Always migrate the cache contents
- Do not migrate the cache contents
How to configure vFRC?
The configuration of vFRC is simple.
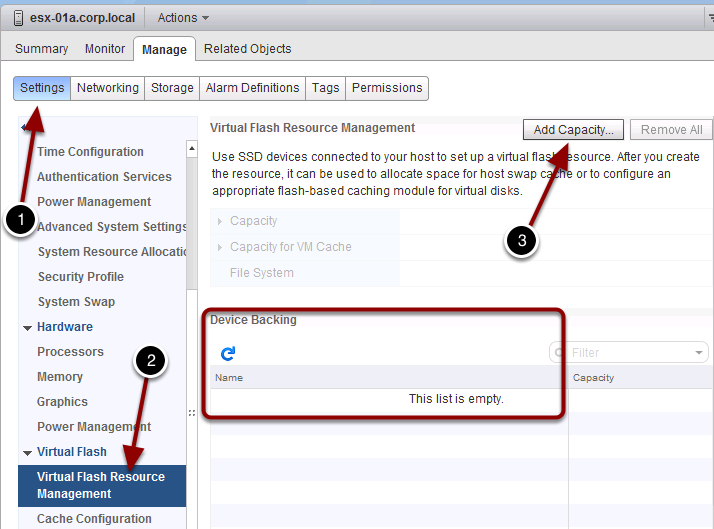
- Log in via Web Client to the vCenter and navigate to Host -> Manage -> Settings (1) -> Virtual Flash Resource Management (2) and Add Capacity (3).
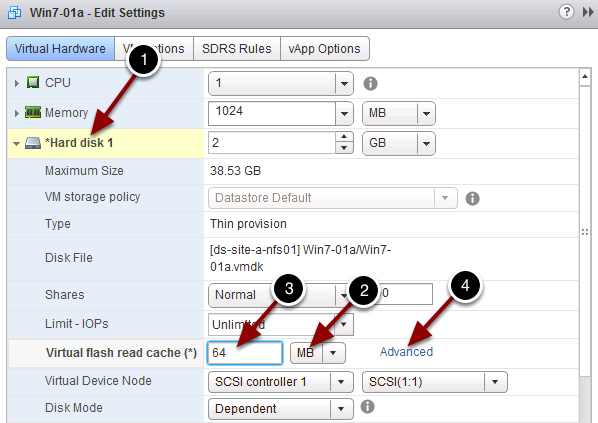
- Right click on Virtual Machine and Select Edit Settings.
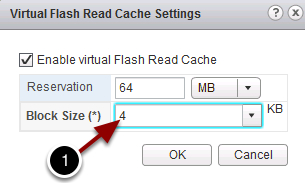
- If you click Advanced (4), you can adjust the vFRC block size. You should match your application I/O pattern with the block size (1). Application I/O pattern can be investigated by using vscsiStats.
- Click OK.
If you want to test vFRC without physical SSD disks, please follow my another post how to emulate SSD. Also you can use VMware Hands-On Lab (HOL): nr 1404.