Yesterday I read 's post on VMware blog and I decided to share some information.
In this post you will find answers for the following questions:
- vCenter 6 Architecture and possible deployment topologies.
- How to protect and build a highly available vCenter Server?
- Links to my another posts to follow deployment and configuring of vCenter Server 6.
vCenter 6 Architecture and possible deployment topologies.
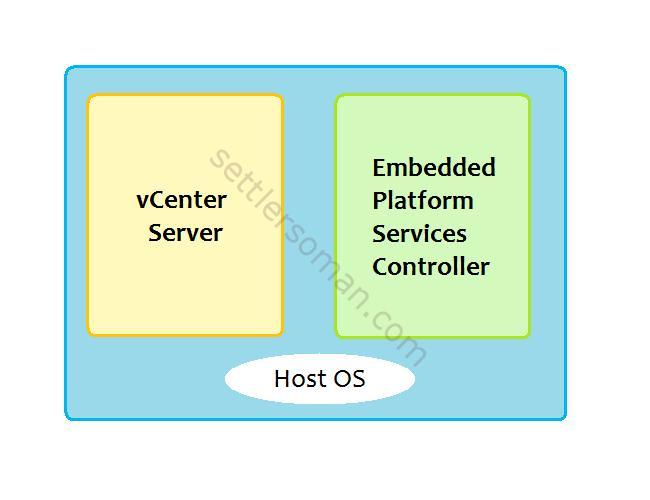
Architecture of vCenter 6 has been reorganized and consolidated. vCenter Server 6 has only two components:
- vCenter Management Server (includes Inventory Service, Web Client).
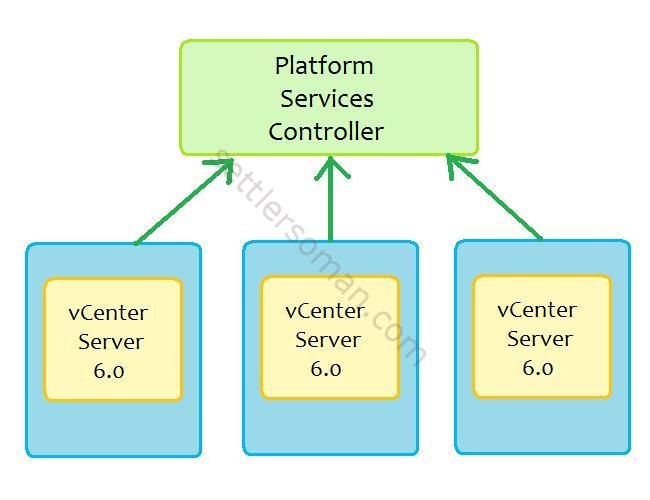
- Platform Services Controller (PSC), formerly vCenter Server Single Sign-On. PSC provides the following infrastructure: Single Sign-On (SSO), Licensing and Certificate Authority. PSC can be shared by multiple vCenter Servers
There are two main deployment models of vCenter Server 6:
- vCenter Server 6 Appliance/Windows Virtual Machine with an Embedded Platform Services Controller.
- vCenter Server 6 (also multiple) Appliance/Windows Virtual Machine with external Platform Services Controller.
vCenter with an Embedded Platform Services Controller is sufficient for most environments - easy to deploy and maintain but the replication between embedded instances is not supported. vCenter with an external Platform Services Controller is recommended for bigger and more complex VMware environment. This deployment model provides replication between PSC and possibility to load balance across them.
Protection and High Availability of vCenter Server 6
There are following possibilities to protect and provide HA for vCenter Server 6:
Backup 🙂
Backup of vCenter should be done to be able to recover it in case of data corruption. To backup vCenter Virtual Machine/Appliance you can use VMware Data Protection Advanced (VDPA) which is included in Essentials+ license or higher! or another 3rd backup solution such NetBackup (my favourite) that provides some very useful features to protect VMware VMs.
Depending on type of vCenter deployment, the vCenter backup can be done as follow:
- vCenter Server 6 Appliance/Windows Virtual Machine with an Embedded Platform Services Controller - VDPA or 3rd backup solution.
- vCenter Server 6 Appliance/Windows Virtual Machine with external Platform Services Controller - VDPA or 3rd backup solution. Snapshots of both VMs should be done at the same time (one backup policy).
- Physical vCenter Server with embedded or external Physical Platform Services Controller. Personally, I do not recommend such deployment topology. In this case, providing a backup solution is much more complex, because the vCenter and PSC backup can not be leveraged on VMware snapshots. Maybe the post: VMware vCenter Appliance (vCSA) or installed on Windows? will convince you to virtualize vCenter 🙂 Also it is possible to migrate vCenter from physical server/virtual machine to the appliance. For more information, please follow post: How to migrate (convert) vCenter with MS Sql to the vCenter Appliance with vPostgres database ?
VMware High Availability (HA)
If the vCenter is virtualized, VMware HA is a standard option to protect vCenter against ESXi host or application failure (using watchdog).
VMware Fault Tolerance (FT)
As mentioned in my another post here, vSphere 6 provides SMP (up to 4vCPU) Fault Tolerance (FT). Even FT protects against hardware failure, it does not protect against application failure. Following vCenter Server for Windows/Appliance Hardware Requirements, Fault Tolerance can be used only for vCenter in "Small Environment" (up to 100 Hosts, 1000 Virtual Machines) because there is 4 vCPU FT limitations (Enterprise Plus License).
Database Clustering
For vCenter servers backed by dedicated or shared Microsoft SQL databases, SQL clustering can be leveraged to provide reduced downtime for unplanned events and for OS patching.
Replication between Platform Services Controller (PSC)
External Platform Services Controllers support replication between them but not provide any built-in load balancer. It is necessary to use a 3rd load balancer.
Clustering vCenter Server
With vCenter 6 (vCenter 5.5 U2 as well) VMware supports 2 node cluster (active/passive) built on Windows Server Failover Cluster.
Deployment Examples for vCenter Server
There are following deployment modes for vCenter Server 6:
Local vCenter Server & PSX High Availability
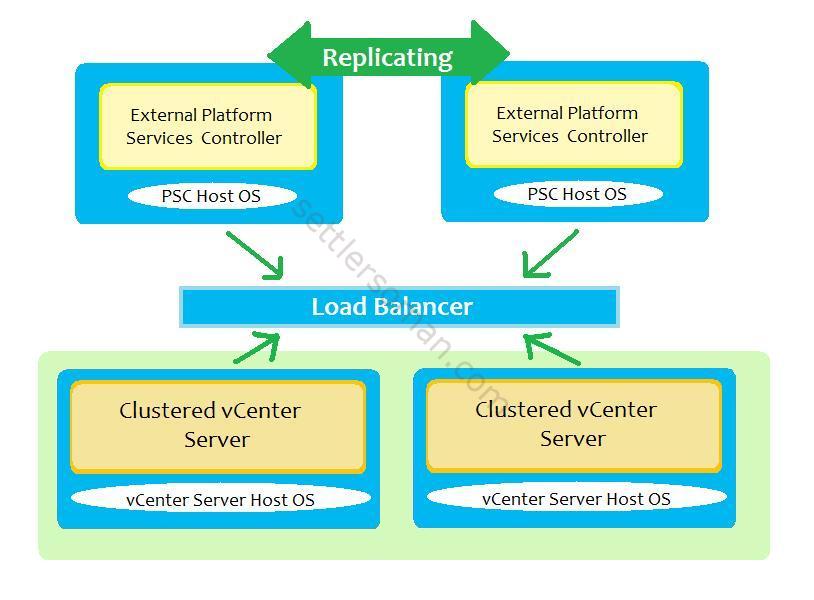
Local vCenter Server & PSX High Availability
This is an example of deployment when failure of a PSC or vCenter (only guest OS) does not impact the usage of the infrastructure. The vCenter cluster (active node) interacts with the PSCs through a load balancer.
Multiple Site vCenter Server and PSC basic Architecture
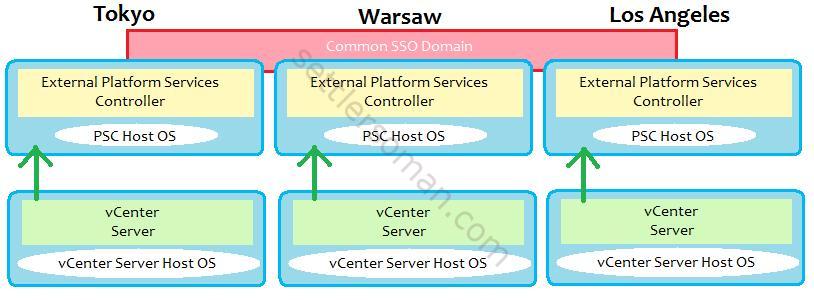
Multiple Site vCenter Server and PSC basic Architecture
In this example each site is independent with PSC replication between sites. The vCenter Server is aware of the site topologies and use the local PSC under normal circumstances but it is possible to move the vCenter Servers between PSCs when needed. This topology allows for Enhanced Linked Mode (ELM) which is facilitated by the PSC. Enhanced Linked Mode provides for a single point of management for all vCenter Servers in the same vSphere domain.
Multiple Site vCenter Server & PSC with High Availability Architecture
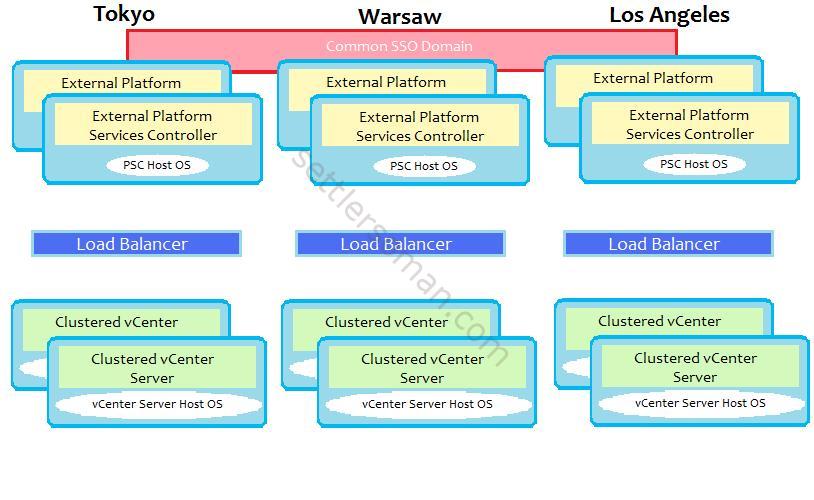
Multiple Site vCenter Server & PSC with High Availability Architecture
In this topology, there is combining the high availability configuration in a local site with the multi site configuration. Each site is populated with at least two PSCs for high availability. vCenter Server nodes are individually clustered with WSFC for HA.
Step by step vCenter 6 Deployment
To deploy and configure vCenter Server 6 please follow one or more below posts:
- How to deploy the vCenter Server 6 Appliance with an Embedded Platform Services Controller?
- vCenter Host Gateway Appliance – Overview and Deployment.
- How to deploy the vCenter Server 6 with External Platform Services Controller?
- How to configure replication between Platform Services Controller (PSC)?
- How to create a vCenter cluster using WSFC?
Conclusion
vCenter Server 6 has a new deployment architecture including high availability possibilities. Clustering vCenter Server and replication between Platform Services Controllers (PSCs) offer a really good way to build a highly available "core" management platform of vSphere environment. Enhanced Linked Mode (ELM) provides a single point of management of multisite vCenter Servers.
vCenter should be protected as good as possible - this is a heart of VMware environment and when vCenter is unavailable, there are some advanced features do not work or limited.