NetApp TR 4128 - vSphere 6 on NetApp MetroCluster 8.3Recently I discussed with my colleague the vSphere Metro Storage Cluster (vMSC) running on NetApp clustered Data ONTAP 8.3 or later as it is supported already by VMware. Our customer wanted to build a highly available virtual infrastructure stretched between two data centers and based on vSphere HA.
In this post you will find answers for the following questions:
- What Is vSphere Metro Storage Cluster (vMSC)?
- What is NetApp MetroCluster?
- NetApp recommendations for VMware HA.
- Failure scenarios.
vSphere Metro Storage Cluster (vMSC) overview
vSphere Metro Storage Cluster (vMSC) is a certified (you should always check/verify compatibility on VMware Storage Compatibility Guide) configuration for stretched storage (synchronized replication) cluster architectures. It means that you can create a vSphere cluster with hosts in two physical data centers (e.g. Tokyo and Yokohama). 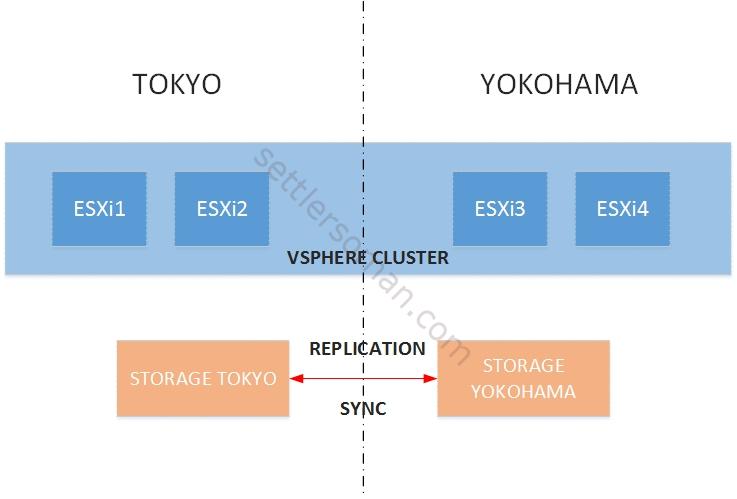 Two vMSC configurations are possible based on how the hosts are connected to the storage arrays.
Two vMSC configurations are possible based on how the hosts are connected to the storage arrays.
- vMSC Uniform - In this configuration each host can access LUNs exported from both the sites. It helps in protecting against a storage failure at a site.
-
vMSC non-Uniform - In this configuration each host can access storage resources available only on its local site.
NetApp Metro Storage Cluster represents vMSC Uniform! 😉 For example EMC VPLEX can be configured as Uniform or non-Uniform.
NetApp MetroCluster overview
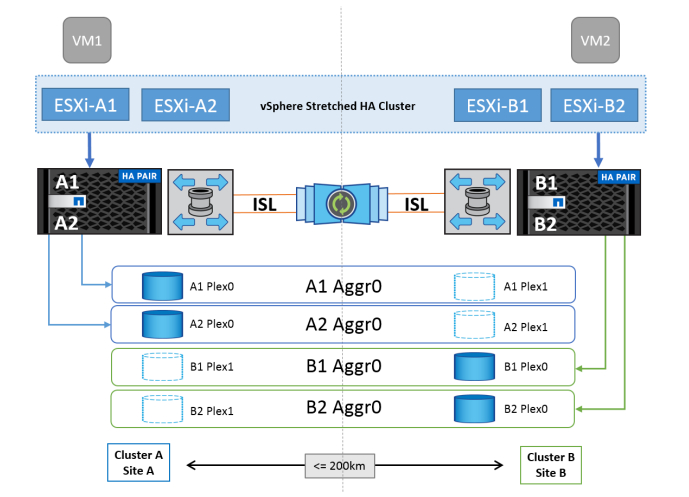
NetApp MetroCluster is a solution (based on synchronous replication, RPO=0) providing automatic recovery for any single storage component failure.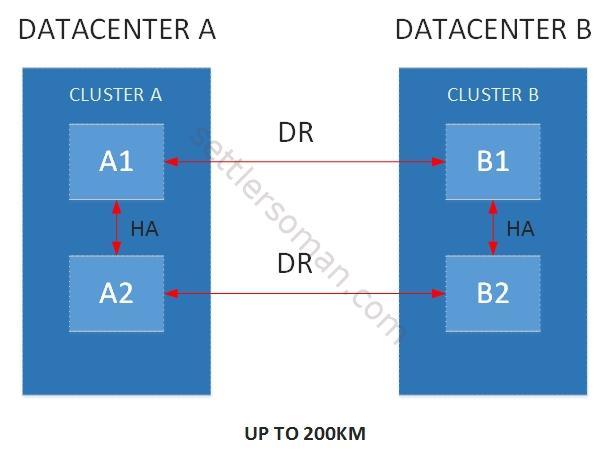
As shown on the above figure, there are two NetApp clusters with two controllers (nodes) in each cluster. Each node has an HA partner in the same local cluster and a DR partner in the remote cluster. A1 and A2 are HA partners, as are B1 and B2. Node A1 and B1 are DR partners, as are A2 and B2. In an HA failover, one of the nodes in the HA pair temporarily takes over the storage and services of its HA partner.
The MetroCluster itself does not detect and initiate a switchover after site failure. It can be done manually (e.g. by you 😉 ) or using software - Tiebreaker. Tiebreaker is a program installed at a third site with independent connections to each of the two clusters. Tiebreaker monitors and detects individual site failure and intersite link (ISL) failure.
NetApp recommendations for vMSC/HA
There are some NetApp recommendations for vSphere 6.0 HA:
Host Failure Detection:
-
Specifying a minimum of two additional isolation addresses and that each ofthese addresses be site local.
Host Isolation Response:
-
The Host Isolation Response setting should be Disabled.
VM Component Protection:
-
The Response for Datastore with PDL setting should be Power Off and Restart VMs.
- The Response for Datastore with APD setting should be Power Off and Restart VMs.
-
The Response for APD Recovery After APD Timeout setting should be Disabled.
For more information please follow two NetApp documents:
- NetApp TR 4375 - MetroCluster for Data ONTAP Version 8.3 Overview and Best Practices
- NetApp TR 4128 - vSphere 6 on NetApp MetroCluster 8.3
Failures scenarios
There are some failure scenarios (more you can find in the mentioned guides):
| Scenario | NetApp Clustered Data ONTAP behavior | VMware HA Behavior |
|---|---|---|
| Single Storage Path Failure | No change in MetroCluster behavior - the datastores continue to be intact from their respective sites. | None |
| Single ESXi Host Failure | No change in MetroCluster behavior - the datastores continue to be intact from their respective sites. | Restart VMs in the local site. |
| ESXi Host Isolation | No change in MetroCluster behavior - The datastores continue to be intact from their respective sites. | Depending on the isolation response configured, the host can choose to power off, shut down the virtual machines, or even leave the virtual machines powered on. |
| Disk Shelf Failure | During this period, there is no impact on the virtual machine I/O operations, but there is degraded performance because the data is being accessed from the remote disk shelf through ISL links. | None |
| Single Storage Controller Failure | The local HA performs failover. | None |
| Complete Site Failure | The storage administrator or tiebreaker performs a switchover. | Virtual machines running at the failed site fail. VMware HA automatically restarts them on the surviving site. |
Conclusion
MetroCluster provides three basic methods for data continuity in the event of planned or unplanned events:
- Redundant components for protection against single component failure
- Local HA takeover for events affecting a single controller (not available in 7-Mode)
- Complete site switchover
At last, there is a possibility to build a highly available VMware infrastructure based on NetApp MetroCluster with two nodes in each site!