EMC ScaleIO is a software-only server-based storage area network (SAN) that converges storage and compute resources to form a single-layer. It uses existing local disks and LANs so that the host can realize a virtual SAN with all the benefits of external storage.
The ScaleIO software consists of three software components: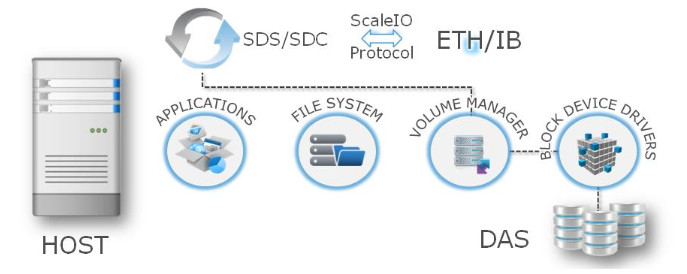
-
Meta Data Manager (MDM) - Configures and monitors the ScaleIO system. The MDM can be configured in a redundant Cluster Mode, with three members on three servers, or in Single Mode on a single server.
- ScaleIO Data Server (SDS) — Manages the capacity of a single server and acts as a back-end for data access. The SDS is installed on all servers contributing storage devices to the ScaleIO system.
- ScaleIO Data Client (SDC) — SDC is a lightweight device driver situated in each host whose applications or file system requires access to the ScaleIO virtual SAN block devices. The SDC exposes block devices representing the ScaleIO volumes that are currently mapped to that host.
ScaleIO can scale to a large number nodes, protects (supports a distributed two-copy redundancy) data against disk and node failures. Main characteristics of EMC ScaleIO are as follows:
Hardware agnostic
ScaleIO supports many options for SDS local storage, including internal disks, directly attached external disks, virtual disks exposed by an internal RAID controller, and partitions within such disks.
Pure block storage implementation
ScaleIO implements a pure block storage layout. Its entire architecture and data path are optimized for block storage access needs.
Clustered and striped volume layout
A ScaleIO volume is a block device that is exposed to one or more hosts and breaks each volume into a large number of data chunks, which are scattered across the SDS cluster’s nodes and disks in a fully balanced manner. This layout minimizes hot spots across the cluster and enables scaling of the overall I/O performance of the system through the addition of nodes or disks.
Protection domains
A large ScaleIO storage pool can be divided into multiple protection domains, each of which contains a set of SDSs. ScaleIO volumes are assigned to specific protection domains. 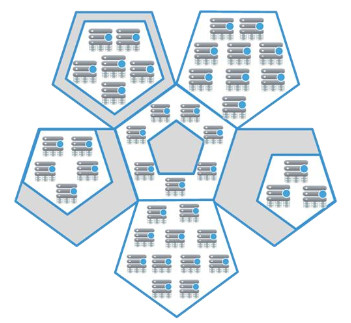 Protection domains are useful for mitigating the risk of a dual point of failure in a two-copy scheme or a triple point of failure in a three-copy scheme. For example, if two SDSs that are in different protection domains fail simultaneously, no data will become unavailable. ScaleIO can overcome a large number of simultaneous disk or node failures as long as they don’t occur within the same protection domain.
Protection domains are useful for mitigating the risk of a dual point of failure in a two-copy scheme or a triple point of failure in a three-copy scheme. For example, if two SDSs that are in different protection domains fail simultaneously, no data will become unavailable. ScaleIO can overcome a large number of simultaneous disk or node failures as long as they don’t occur within the same protection domain.
Main features of EMC ScaleIO:
- Snapshots - snapshot is essentially a volume of its own. For each ScaleIO volume, you can create multiple fully rewritable, redirect-on-write snapshots.
You can use ScaleIO to take a set of consistent snapshots of a given set of volumes across multiple servers. You can also take a snapshot of the entire cluster’s volumes in a consistent manner. If crash consistency is acceptable, there is no need to stop, pause, or freeze I/O traffic to hosts, for any application activities, during snapshot creation.
-
Thick and thin provisioning
- Fault sets - is a group of SDSs that are likely to go down together. ScaleIO mirroring ensures high data availability. If an SDS goes down, the mirrored data is immediately available from another SDS.
- RAM read cache - this feature allocates space on the storage devices for caching reads or writes. You can configure RAM cache for an entire storage pool or in individual SDSs. By default, the RAM cache size is 128 MB in all the SDSs.
- IOPS Limiter - sets maximum IOPS or bandwidth values per client/volume. If an application attempts to consume more than its allowance, ScaleIO smoothly limits the application’s IOPS or bandwidth workload.
- Graphical User Interface (GUI)
- Support VMware, Hyper-V and also OpenStack
- Encryption